As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, innovative technologies are being developed to improve patient outcomes and streamline clinical workflows. One such breakthrough is the 2025 AI Detection Tool, designed to identify rare carcinoid tumors that may be missed by traditional imaging methods. In this blog post, we'll delve into the world of carcinoid tumors, explore the limitations of conventional diagnostic techniques, and discuss the potential of AI-powered detection tools to transform cancer diagnosis.
Understanding Carcinoid Tumors
Carcinoid tumorsare often asymptomatic, making early detection challenging. If left untreated, these tumors can lead to severe complications, such as carcinoid syndrome, which is characterized by flushing, diarrhea, and heart valve abnormalities.
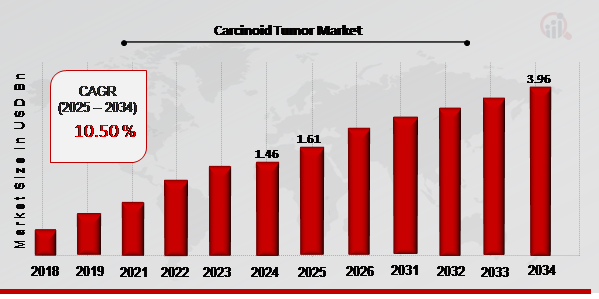
Limitations of Traditional Imaging Methods
Conventional imaging techniques, including computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) scans, are commonly used to diagnose carcinoid tumors. However, these methods have limitations. For instance:
- Small tumor size: Carcinoid tumors are often small, making them difficult to detect using traditional imaging methods.
- Location: Tumors located in hard-to-reach areas, such as the small intestine, can be challenging to visualize.
- Image quality: Poor image quality can lead to false negatives or false positives, resulting in delayed or inaccurate diagnoses.
The Emergence of AI-Powered Detection Tools
The 2025 AI Detection Tool is a cutting-edge technology designed to overcome the limitations of traditional imaging methods. This innovative tool utilizes artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to analyze medical images and detect carcinoid tumors with greater accuracy. The AI-powered detection tool offers several benefits, including:
- Improved sensitivity: AI-powered detection tools can identify small tumors that may be missed by traditional imaging methods.
- Enhanced specificity: AI algorithms can reduce false positives and false negatives, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
- Increased efficiency: AI-powered detection tools can analyze large amounts of medical data quickly, streamlining the diagnostic process.
Clinical Applications and Future Directions
The 2025 AI Detection Tool has the potential to revolutionize cancer diagnosis, particularly for rare and hard-to-detect tumors like carcinoid tumors. Clinical applications of this technology include:
- Early detection: AI-powered detection tools can facilitate early detection, enabling timely treatment and improving patient outcomes.
- Personalized medicine: AI algorithms can analyze individual patient data to provide personalized treatment recommendations.
- Cancer research: AI-powered detection tools can aid researchers in identifying new cancer biomarkers and developing more effective treatments.
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, we can expect to see further innovations in AI-powered detection tools. Future directions may include:
- Integration with electronic health records (EHRs): Seamless integration with EHRs can facilitate data sharing and analysis, improving patient care.
- Development of specialized AI algorithms: Specialized AI algorithms can be developed to detect specific types of cancer, such as lung or breast cancer.
- Expansion to other medical specialties: AI-powered detection tools can be applied to other medical specialties, such as cardiology and neurology.
Conclusion
The 2025 AI Detection Tool represents a significant breakthrough in cancer diagnosis, offering improved sensitivity, specificity, and efficiency. As the healthcare industry continues to innovate, we can expect to see further advancements in AI-powered detection tools, leading to better patient outcomes and improved clinical workflows. By embracing these innovative technologies, healthcare professionals, procurement managers, hospital administrators, manufacturers, and regulatory bodies can work together to transform cancer diagnosis and treatment.
BROWSE MORE HEALTHCARE REPORTS:






